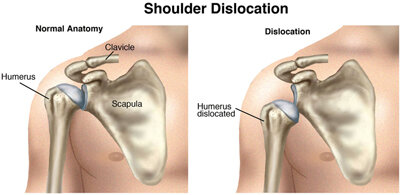
The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body and is the most likely joint to dislocate. A dislocation is the separation of 2 bones where they meet at a joint. Shoulder dislocations most often occur during contact sports, but everyday accidents, such as falls, also can cause the joint to dislocate. Athletes, nonathletes, children, and adults can all dislocate their shoulders. A dislocated shoulder usually requires the assistance of a health care professional to guide the joint back into place. After the joint is realigned, a physical therapist directs the rehabilitation of the shoulder, and helps the affected individual prevent reinjury.
CAUTION: A shoulder dislocation requires immediate medical attention, especially if you experience:
Numbness in your arm or hand
Discoloration of your arm or hand
A feeling of coldness in your arm
Any of these conditions may indicate injury to a nerve or blood vessel. Seek medical help immediately.
What is a Shoulder Dislocation?
The shoulder includes the clavicle (collar bone), scapula (shoulder blade), and humerus (upper-arm bone). The rounded top of the humerus and the cup-like end of the scapula fit together like a ball and socket. A shoulder dislocation can occur with an injury, such as when you "fall the wrong way" on your shoulder or outstretched arm, forcing the shoulder beyond its normal range of movement and causing the humerus to come out of the socket. Dislocation can result in damage to many parts of the shoulder, including the bones, the ligaments, the labrum (the ring of cartilage that surrounds the socket), and the muscles and tendons around the shoulder joint.
Joints may dislocate when a sudden impact causes the bones in the joint to shift out of place. Dislocations are among the most common traumatic injuries affecting the shoulder.
How Does It Feel?
With most shoulder dislocations, you will feel the humerus coming out of the socket, followed by:
Pain
Inability to move the arm
Awkward appearance of the shoulder
If you have any signs or symptoms of a nerve or blood vessel injury, as listed above, seek immediate medical attention.
The humerus usually remains out of the socket until a physician guides it back into place. X-rays are routinely taken after the dislocation is moved back into place to make sure that you don’t have a fracture.
Occasionally, the shoulder may go back into place on its own. You might not even realize that you have dislocated your shoulder; you may only feel that you have injured it. If you have injured your shoulder and have pain, seek medical attention.
How Can a Physical Therapist Help?
After the dislocated humerus has been moved back into position, your arm will be placed in a sling to protect you from reinjury and to make your shoulder more comfortable. Your physical therapist can review your health and injury history and conduct a physical examination to determine your rehabilitation needs. Based on the results of the examination and your goals, your physical therapist will guide you through a rehabilitation program to restore your mobility, strength, joint awareness, and sport-specific skills. Your therapist also will show you how to control your pain and relieve any inflammation.
Your treatment program may include:
Range-of-motion exercises. Swelling and pain can reduce your shoulder movement. Your physical therapist will teach you how to perform safe and effective exercises to restore full range of motion to your shoulder. Your physical therapist might apply manual (hands-on) therapy to help decrease pain in the shoulder.
Strengthening exercises. Poor muscle strength can cause the shoulder joint to remain unstable and possibly reinjure it. Based on how severe your injury is and where you are on the path to recovery, your physical therapist can determine which strengthening exercises are right for the rehabilitation of your shoulder.
Joint awareness and muscle retraining. Specialized exercises help your shoulder muscles relearn how to respond to sudden forces. Your physical therapist will design individualized exercises to help you return to your regular activities.
Activity- or sport-specific training. Depending on the requirements of your job or the type of sports you play, you might need additional rehabilitation tailored to the demands your activities place on your shoulder. Your physical therapist can develop a program that takes all of these demands (as well as your specific injury) into account. For example, if you are an overhead thrower, such as a baseball pitcher, your physical therapist will guide you through a throwing progression and pay specific attention to your throwing mechanics.
Can This Injury or Condition Be Prevented?
Shoulder dislocations are dependent on how loose the shoulder is, and are more likely to occur during sports or aggressive activities. Your physical therapist can advise you about the positions that frequently cause dislocations, and teach you ways to reduce your risk of dislocation. See your physical therapist if you:
Have pain in your shoulder, especially when performing forceful activities
Have symptoms that feel as though your shoulder is "slipping," “shifting,” or "moving"
Hear a popping sound in your shoulder accompanied by pain
Shoulder dislocations are dependent on how loose the shoulder is, and are more likely to occur during sports or aggressive activities. Your physical therapist can advise you about the positions that frequently cause dislocations, and teach you ways to reduce your risk of dislocation. See your physical therapist if you:
Have pain in your shoulder, especially when performing forceful activities
Have symptoms that feel as though your shoulder is "slipping," “shifting,” or "moving"
Hear a popping sound in your shoulder accompanied by pain
If you already have a history of shoulder dislocation, you are at a greater risk for reinjury if your shoulder does not heal properly or if you do not regain your normal shoulder strength or joint awareness. Research shows that a high percentage of dislocated shoulders will dislocate again. Physical therapists play an important role in helping people prevent recurring shoulder problems.
If you return to sports or activities too soon following injury, you could cause a reinjury. Your physical therapist can determine when you are ready to return to your activities and sports by making sure that your shoulder is strong and ready for action. Your physical therapist may recommend a shoulder brace to allow you to gradually and safely return to your previous activities.
Real Life Experiences
Bob is a 25-year-old salesman and a competitive snowboarder. Recently, he spent the day snowboarding with friends. Toward the end of the day, the front edge of his snowboard caught in the snow, throwing him off-balance. As he fell, he reached out his right arm to break the fall. He felt a pop in his shoulder, and a sharp pain. He felt like his shoulder was out of place. His friend called the ski patrol, who guided him safely down the mountain and took him to the local emergency department. X-rays showed that Bob’s shoulder was dislocated. The emergency physician put Bob’s shoulder back into place and secured it in a sling. He recommended that Bob see a physical therapist for rehabilitation.
At his first visit, Bob’s physical therapist reviews the history of his injury and his general health and performs a thorough examination. Because Bob's goal is to return to an active lifestyle as soon as possible, she develops a rehabilitation plan of care to restore the mobility, strength, and function of Bob's shoulder.
Bob’s physical therapist applies a cold pack to relieve his pain, and performs gentle hands-on range-of-motion exercises to the shoulder area. She also teaches Bob a few gentle movement and strengthening exercises he can do himself.
Once Bob's pain has decreased, his rehabilitation focuses on restoring the dynamic stability of his shoulder through movement re-education and drills, and strengthening of the shoulder area. Bob's physical therapist chooses specific movements and exercises to gently restore his shoulder range of motion, while allowing the shoulder to heal. Particular emphasis is placed on educating Bob and avoiding stretches and activities that put too much stress on the injured parts of his shoulder.
Working with his physical therapist, Bob steadily increases his shoulder strength and range of motion.
At 12 weeks postinjury, Bob’s physical therapist informs him he is ready to return to training for competition. She advises him to be aware of his shoulder movements and to use the techniques he learned in physical therapy to avoid reinjury.
Bob begins to train for the next season’s snowboarding competitions and is able to practice at his previous level—with his shoulder returned to its full strength and mobility.
This story was based on a real-life case. Your case may be different. Your physical therapist will tailor a treatment program to your specific case.
What Kind of Physical Therapist Do I Need?
All physical therapists are prepared through education and experience to treat patients who have a dislocated shoulder. You may want to consider:
A physical therapist who is experienced in treating people with musculoskeletal problems. Some physical therapists have a practice with an orthopedic focus.
A physical therapist who is a board-certified clinical specialist or who completed a residency or fellowship in orthopedic or sports physical therapy. This physical therapist has advanced knowledge, experience, and skills that may apply to your condition.
You can find physical therapists who have these and other credentials by using Find a PT, the online tool built by the American Physical Therapy Association to help you search for physical therapists with specific clinical expertise in your geographic area.
General tips when you're looking for a physical therapist (or any other health care provider):
Get recommendations from family and friends or from other health care providers.
When you contact a physical therapy clinic for an appointment, ask about the physical therapists' experience in helping people with shoulder dislocation.
During your first visit with the physical therapist, be prepared to describe your symptoms in as much detail as possible, and say what makes your symptoms worse.
Further Reading
The American Physical Therapy Association (APTA) believes that consumers should have access to information that could help them make health care decisions and also prepare them for their visit with their health care provider.
APTA has determined that the following articles provide some of the best scientific evidence for how to treat shoulder dislocation. The articles report recent research and give an overview of the standards of practice for treatment both in the United States and internationally. The article titles are linked either to a PubMed* abstract of the article or to free access of the full article, so that you can read it or print out a copy to bring with you to your health care provider.
Khiami F, Gerometta A, Loriaut P. Management of recent first-time anterior shoulder dislocations. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(1 Suppl):S551–S557. Article Summary on PubMed.
Robinson CM, Seah M, Akhtar MA. The epidemiology, risk of recurrence, and functional outcome after an acute traumatic posterior dislocation of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2011;93(17):1605–1613. Article Summary on PubMed.
Godin J, Sekiya JK. Systematic review of rehabilitation versus operative stabilization for the treatment of first-time anterior shoulder dislocations. Sports Health. 2010;2:156–165. Free Article.
Brumitt J, Sproul A, Lentz P, et al. In-season rehabilitation of a division III female wrestler after a glenohumeral dislocation. Phys Ther Sport. 2009;10:112–117. Article Summary on PubMed.
Hovelius L, Olofsson A, Sandström B, et al. Nonoperative treatment of primary anterior shoulder dislocation in patients forty years of age and younger: a prospective twenty-five year follow up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90:945–952. Article Summary on PubMed.
Robinson CM, Howes J, Murdoch H, Will E, Graham C. Functional outcome and risk of recurrent instability after primary traumatic anterior shoulder dislocation in young patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(11):2326–2336. Article Summary on PubMed.
Robinson CM, Howes J, Murdoch H, Will E, Graham C. Functional outcome and risk of recurrent instability after primary traumatic anterior shoulder dislocation in young patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:2326–2336. Article Summary on PubMed.
Millar AL, Lasheway PA, Eaton W, Christensen F. A retrospective, descriptive study of shoulder outcomes in outpatient physical therapy. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2006;36:403–414. Article Summary on PubMed.
Buss DD, Lynch GP, Meyer CP, Huber SM, Freehill MO. Nonoperative management for in-season athletes with anterior shoulder instability [erratum in: Am J Sports Med. 2004;32:1780]. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32:1430–1433. Article Summary on PubMed.
Gibson K, Growse A, Korda L, Wray E, MacDermid JC. The effectiveness of rehabilitation for nonoperative management of shoulder instability: a systematic review. J Hand Ther. 2004;17:229–242. Article Summary on PubMed.
*PubMed is a free online resource developed by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). PubMed contains millions of citations to biomedical literature, including citations in the National Library of Medicine’s MEDLINE database.
Authored by Jason Lunden, PT, DPT, board-certified sports clinical specialist. Reviewed by the editorial board.